Sorry, no sales person is available right now to take your call. Pls leave a message and we will reply to you via email as soon as possible.
How to Choose High-Frequency, High-Speed PCB Materials
As microprocessor and signal conversion/transmission device speeds increase, the operating speeds of digital circuits have reached a higher level: 100Gbps. The use of general PCB materials will not meet the requirements of high-speed signals, and the choice of circuit board materials will determine product performance.
Choosing PCB materials must strike a balance between meeting design requirements, mass producibility, and cost. Simply put, design requirements include both electrical and structural reliability. The material issue is particularly crucial when designing very high-speed PCBs (frequencies above GHz). For example, the commonly used FR-4 material may exhibit significant dielectric loss (Df) at frequencies of several GHz, making it unsuitable.
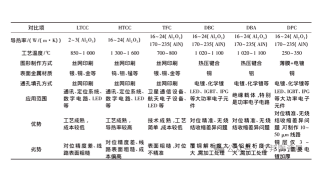
Loss of Different Materials
For instance, a 10Gb/s high-speed digital signal is a square wave, which can be seen as a superposition of sine wave signals of different frequencies. Therefore, 10Gb/s encompasses many signals of different frequencies: a fundamental signal of 5GHz, a third-order signal of 15GHz, a fifth-order signal of 25GHz, a seventh-order signal of 35GHz, etc. Maintaining the integrity of digital signals and the steepness of their rising and falling edges is as important as low-loss, low-distortion transmission in radio frequency microwaves (where the high-frequency harmonic components of digital signals reach microwave frequency bands). Thus, in many ways, the material selection for high-speed digital circuit PCBs is similar to the requirements for radio frequency microwave circuits.
Time Domain/Frequency Domain
In practical engineering operations, the selection of high-frequency materials seems simple but involves many factors to consider. Through this introduction, PCB design engineers or high-speed project leaders can gain a certain understanding of material characteristics and selection. They should understand the electrical, thermal, and reliability properties of materials. By reasonably using lamination, they can design a product with high reliability and good processability, optimizing the consideration of various factors.
Below are the main factors to consider when selecting suitable materials:
- Manufacturability:
- Various product-matching performance (electrical, stability, etc.):
- Timely availability of materials:
- Cost factor:
- Applicability of laws and regulations:
Among the above factors, the operating speed of high-speed digital circuits is the primary consideration for PCB selection. The higher the circuit speed, the lower the selected PCB Df value should be. Circuit materials with medium to low loss will be suitable for 10Gb/s digital circuits; materials with even lower loss are suitable for 25Gb/s digital circuits; and materials with ultra-low loss will accommodate faster high-speed digital circuits, with speeds of 50Gb/s or higher.
From the perspective of material Df:
- Circuit materials with Df between 0.01 and 0.005 are suitable for digital circuits up to 10Gb/s.
- Circuit materials with Df between 0.005 and 0.003 are suitable for digital circuits up to 25Gb/s.
- Circuit materials with Df not exceeding 0.0015 are suitable for 50Gb/s or even higher-speed digital circuits.
Commonly used high-speed materials include:
- Rogers: RO4003, RO3003, RO4350, RO5880, etc.
- TUC: Tuc862, 872SLK, 883, 933, etc.
- Panasonic: Megtron4, Megtron6, etc.
- Isola: FR408HR, IS620, IS680, etc.
- Nelco: N4000-13, N4000-13EPSI, etc.
- Dongguan Shengyi, Taizhou Wangling, Taixing Microwave, etc.