Sorry, no sales person is available right now to take your call. Pls leave a message and we will reply to you via email as soon as possible.
Understanding 99.6% Alumina Ceramic Substrates: A Comprehensive Guide
You’ve likely heard of 99.6% alumina ceramic substrates—but how do they differ from ordinary ceramic boards? The distinctions are significant, rooted in their superior material properties and specialized applications. Let’s break down everything you need to know about 99 alumina ceramic substrates, including their background, technical challenges, real-world uses, and manufacturing breakthroughs.
Background of 99.6% Alumina Ceramic Substrates
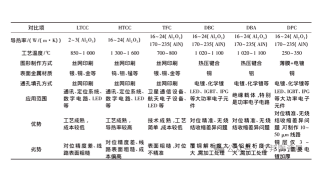
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) have a history spanning over 100 years. As industries sought alternatives to polymer-based substrates—especially for high-temperature, high-power, and high-reliability scenarios—96% alumina ceramic substrates emerged as a cost-effective solution and gained widespread adoption. Leading manufacturers of 96% alumina ceramic substrates include Japan’s Kyocera, U.S.-based CoorsTek, Germany’s CeramTec, and domestic producers like Guangdong Sanhuan Group and Tsinghua Yuke.
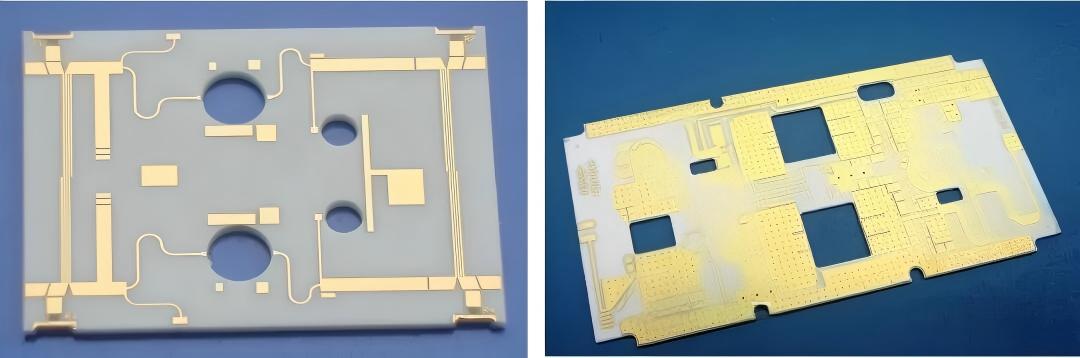
However, 99.6% alumina ceramic—offering superior performance (higher density, better thermal conductivity, and stronger insulation) than 96% alumina—long remained unproduced in China due to formidable technical barriers. This gap limited the development of high-end electronic devices that relied on ultra-reliable ceramic substrates.
Technical Challenges of 99 Alumina Ceramic Substrates
Producing ultra-thin 99.6% alumina ceramic substrates (≤0.1mm) is a core technical challenge, spanning four key processes: raw material formulation, forming, sintering, and grinding. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
- Raw Material Purity Requirements: 96% alumina substrates typically use 99.9% pure alumina powder, blended with silica, Suzhou clay, and calcium carbonate to lower sintering temperatures and improve slurry plasticity for tape casting. In contrast, 99.6% alumina requires ultra-high-purity raw materials (alumina purity ≥99.99%) that traditional formulations cannot meet—impurities would severely degrade its insulation and thermal conductivity.
- Forming & Sintering Difficulties: Conventional tape casting and injection molding fail to achieve the precision needed for ≤0.1mm thickness in 99.6% alumina. High purity complicates densification during sintering; the material is prone to warping, cracking, or poor dimensional stability if the sintering temperature and atmosphere are not strictly controlled.
- Overcoming these hurdles has been a longstanding industry challenge. When successfully produced, 99 alumina substrates solve critical performance bottlenecks for manufacturers in high-end electronic fields.
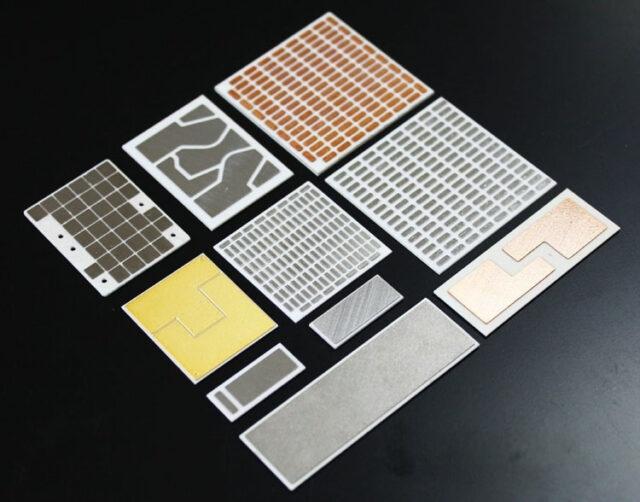
Key Application Scenarios of 99 Alumina Ceramic Substrates
The exceptional properties of 99 alumina ceramic substrates—high thermal conductivity (≥30 W/m·K), excellent electrical insulation, high temperature resistance (up to 1600°C), and good mechanical strength—make them indispensable in several high-demand industries. Typical application scenarios include:
- Power Electronics: Serves as the core substrate for insulated gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs), power modules, and rectifiers—key components in power grids, industrial frequency converters, and high-voltage power supplies. Specifically, it is widely used in 1200V-6500V high-voltage, 50A-1500A high-current IGBT modules, where its technical advantages are fully exerted: the thermal conductivity of 99 alumina substrates reaches 30-35 W/m·K (higher than 96% alumina substrates by 15%-20%), which can efficiently dissipate the heat flux (up to 200 W/cm²) generated by high-power operation, ensuring the module’s working junction temperature is stably controlled at -40℃~150℃. Meanwhile, its volume resistivity ≥10¹⁴Ω·cm and breakdown voltage ≥20kV/mm provide reliable electrical insulation, avoiding leakage and short-circuit risks under high-voltage conditions. In addition, the substrate’s flatness ≤5μm/100mm and dimensional tolerance ±0.02mm ensure precise bonding with chips and metal layers, improving the long-term stability and service life of power electronic devices (typical service life ≥20,000 hours under rated working conditions).
- Automotive Electronics: Critical for new energy vehicle (NEV) powertrains, including on-board chargers (OBC), motor controllers, and battery management systems (BMS). The substrate’s resistance to high temperatures and vibration ensures reliable operation in harsh automotive environments.
- Aerospace & Avionics: Used in aircraft engine control systems, satellite communication equipment, and radar modules. It meets the industry’s strict requirements for lightweight, high reliability, and resistance to extreme temperatures and radiation
- LED Lighting: Applied in high-power LED chips (e.g., street lamps, industrial lighting, and automotive headlights). The substrate’s superior thermal conductivity prevents LED chip overheating, extending its service life and maintaining luminous efficiency.
- Medical Devices: Utilized in high-precision medical equipment such as laser therapy devices, ultrasonic probes, and diagnostic instruments. Its biocompatibility, chemical inertness, and insulation properties ensure safety and stability in medical applications.
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: Used as a carrier substrate for semiconductor wafers during etching, deposition, and packaging processes. It provides stable support and heat dissipation, ensuring the precision of semiconductor manufacturing.
Kinji: Expertise in Advanced Ceramic Substrates
As a specialized manufacturer of high-performance circuit boards—particularly ceramic substrates—Kinji addresses industry pain points by selecting ultra-high-purity alumina ceramic sheets and leveraging cutting-edge manufacturing processes, including advanced thick-film technology and Direct Plated Copper (DPC) ceramic manufacturing.
These capabilities enable precision circuit patterning (line width/space ≤50μm), 3D structuring, and dam-ring ceramic processing—critical for meeting the demands of high-end application scenarios. Recent breakthroughs in production technology have also driven down costs significantly, making 99 alumina ceramic substrates more accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises.
For more details on 99 alumina ceramic substrate production, customization, and technical support, consult Kinji.