Sorry, no sales person is available right now to take your call. Pls leave a message and we will reply to you via email as soon as possible.
Ceramic Substrates for EV Power and IGBT Modules
Introduction
Ceramic substrates, made from advanced ceramic materials such as alumina (Al₂O₃), aluminum nitride (AlN), and silicon nitride (Si₃N₄), are widely used in high‑power electronic packaging. Through specialized processes—including Direct Bonded Copper (DBC), Active Metal Brazing (AMB), and Direct Plated Copper (DPC)—copper layers are bonded to the ceramic surface to form precise circuit patterns. With their unique thermal, mechanical, and electrical properties, ceramic substrates have become the ideal choice for demanding power electronics applications, particularly in electric vehicle (EV) power modules.

Figure 1. Ceramic PCB samples with copper patterning for high-power module applications
Core Properties
Thermal Performance
- High Thermal Conductivity: Ranging from 23–350 W/m·K. For example, AlN reaches up to 170 W/m·K, far exceeding traditional organic substrates such as FR4 (0.3 W/m·K). This enables efficient heat dissipation for high‑power devices like IGBTs and MOSFETs, preventing thermal failure.
- Low Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE): Typically below 8 ppm/K, closely matching silicon chips to reduce thermal stress and enhance reliability.
- High Temperature Resistance: Stable operation above 600°C, suitable for extreme environments such as automotive and aerospace.
Mechanical Performance
- High Strength and Hardness: Excellent mechanical strength and wear resistance, capable of withstanding vibration, impact, and mechanical stress.
- Dimensional Stability: Maintains structural integrity, preventing circuit deformation or fracture.
- Corrosion Resistance: Chemically stable, resistant to acids, alkalis, oxidation, and radiation.
Electrical Performance
- High Insulation: Breakdown voltage exceeding 6000 kV/mm, ensuring reliable high‑voltage isolation.
- Low Dielectric Loss: As low as 0.002, suitable for high‑frequency signal transmission (e.g., 5G), minimizing signal attenuation.
- Excellent Conductivity: Copper layers support high current density, improving efficiency and power density.
Key Applications
Ceramic substrates are extensively used in power modules, especially in electric and hybrid vehicles:
- EV Power Modules: Applied in inverters, battery management systems, and drive control modules. They support high‑voltage, high‑power conversion (e.g., 800V platforms), ensuring thermal management and electrical insulation while enhancing overall vehicle efficiency and reliability.
- Other Fields: Industrial power supplies, renewable energy, aerospace, and communication equipment, meeting requirements for high power density, high frequency, and high‑temperature environments.
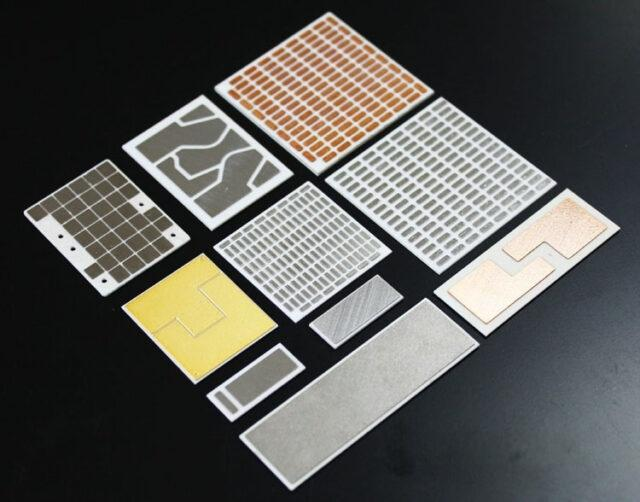
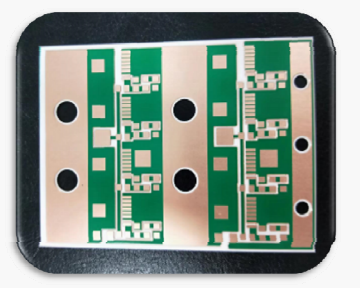
Figure 2. Ceramic PCBs for EV power modules and high‑power electronics
Manufacturing Processes and Material Comparison
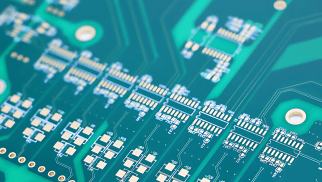
Ceramic substrates employ DBC, AMB, and DPC technologies to achieve strong copper‑ceramic bonding and precise circuit formation. Common ceramic materials include:
| Material Type | Key Properties | Advantages & Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) | Cost‑effective, balanced performance; lower thermal conductivity (20–30 W/m·K) | Advantage: low cost, widely used; Disadvantage: limited thermal performance, unsuitable for extreme heat. |
| Aluminum Nitride (AlN) | High thermal conductivity (170 W/m·K); CTE matches silicon; high flexural strength | Advantage: excellent heat dissipation, high reliability; Disadvantage: higher cost, strict process requirements. |
| Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) | Superior flexural strength and fracture toughness; good thermal conductivity (60–90 W/m·K); strong thermal shock resistance | Advantage: outstanding mechanical properties, ideal for high‑stress environments; Disadvantage: high cost, complex processing. |
Conclusion
Ceramic substrates have proven indispensable in high‑power electronics, particularly in electric vehicle power modules. Their superior thermal management, mechanical strength, and electrical insulation ensure reliability and efficiency in demanding environments. For engineers seeking practical solutions, the following products exemplify high‑performance ceramic PCB technology.
Recommended Products
2‑Layer Alumina DBC Ceramic Copper Clad PCB for Power Circuits
- Thickness: 1.0 mm
- Copper: 8.5/8.5 oz (0.3/0.3 mm)
- Application: High‑power supply circuits
2‑Layer Alumina DBC PCB for Power Circuits — Tap to order
2‑Layer Alumina DBC Ceramic Copper Clad PCB for IGBT Modules
- Thickness: 0.635 mm
- Copper: 8.5/8.5 oz (0.3/0.3 mm)
- Application: IGBT power modules
2‑Layer Alumina DBC PCB for IGBT Modules — Tap to order
Whether you're prototyping a new design or preparing for high-volume production, our engineering team is here to support your ceramic PCB needs. From solder mask customization to stack-up optimization, we deliver boards that perform reliably in demanding environments.
Need custom ceramic PCBs or full manufacturing support?
Tap the product images above to place your order, or contact us to discuss your project.